skip to main |
skip to sidebar
Abaixo as tabelas verdade para os operadores lógicos AND, OR e NOT.
Operador AND
Operador OR
Operador NOT
IDE Navigation
F2 Object Browser
F4 Property Window
Shift+F4 Property Pages
F6 Change Window (Split Window Mode)
F7 Code Window
Shift+F7 Object (Design) Window
Ctrl+D Add File
Ctrl+E Menu Editor
Ctrl+G Immediate Window
Ctrl+L Call Stack (When in RUN mode)
Ctrl+R Solutions Explorer
Ctrl+T Component Window
Ctrl+PgUp Go to Previous Sub/Function/Property (Declaration Line)
Ctrl+PgDn Go to Next Sub/Function/Property (Declaration Line)
Ctrl+Up Go to Previous Sub/Function/Property (First Line after Declaration)
Ctrl+Dn Go to Next Sub/Function/Property (First Line after Declaration)
Code Navigation
Shift+F2 Definition
Ctrl+Shift+F2 Last Cursor Position
F3 Find Next (Last searched item)
Shift+F3 Find Previous (Last searched item)
Ctrl+F3 Find Next (Current Selection)
Ctrl+Shift+F3 Find Previous (Current Selection)
Shift+F10 Context Menu (occasional erratic behaviour, use ContextMenuKey instead)
Form Designer
Shift+Arrow Resize Control
Ctrl+Arrow Move Control (Direction)
Code Edit Shortcuts
Ctrl+Space Complete Word
Ctrl+J List Properties/Methods
Ctrl+Shift+J List Constants
Ctrl+I Quick Info
Ctrl+Shift+I Parameter Info
Run
F5 Start/Continue
Ctrl+F5 Start with Full Compile
Ctrl+Break Break
Shift+F5 Restart
Debug
F8 Step Into
Shift+F8 Step Over
Ctrl+Shift+F8 Step Out
Ctrl+F8 Run To Cursor
Ctrl+W Edit Watch
Shift+F9 Quick Watch
F9 Add/Remove Breakpoint
Ctrl+Shift+F9 Clear All Breakpoints
Ctrl+F9 Set Next Statement
Ctrl+RightArrow Show End Variable Value (tooltip displying variable value is truncated,
use left arrow to view start again)
Service Pack 6 for Visual Basic 6.0
Service Pack 6 for Visual Basic 6.0 contém as últimas atualizações para o Visual Basic 6.0. Esta atualização é recomenda para todos os usuários do Visual Basic 6.0.
Clique no Link para baixa do próprio site da Microsoft.
Service Pack para Visual Basic 6
Clique no Link para baixa do próprio site da Microsoft.
Service Pack para Visual Basic 6
Aula 1 - Exercício Extra_01
[] Desenvolver um projeto que solicite o nome, as notas de 4 bimestres, e as faltas de um aluno. Calcule a média e escreva em um label (Situação) "Aprovado" se a média for maior >= 7 e o número de faltas menor que 5 (da seguinte forma EX: Pedro você foi "Aprovado" com a Média 7) caso contrário "Reprovado".
Aluno: |_____________________________|
1 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
2 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
3 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
4 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
Média Final: |______________________________|
Total de Faltas |____________________________|
Situação |_________________________________|
Aluno: |_____________________________|
1 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
2 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
3 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
4 bim |______________________________| Faltas |_________ |
Média Final: |______________________________|
Total de Faltas |____________________________|
Situação |_________________________________|
Aula1 - Visual Basic
Curso: Técnico em Informática
Disciplina: Linguagem de Programação ( Visual Basic )
Carga Horária: 76 Hrs
Docente Responsável: Francismar Nascimento
Aprendemos a criar um novo projeto (File / New Project - CTRL + N) e utilizar o opção Standard EXE.
Para salvar o Projeto (File / Save Project )
Para abrir um Projeto Existente ( File / OPen Projec
t - CTRL + O)
Para fechar o Projeto atual (ALT + F4)
Dicas Gerais
:: Para abrir as janelas de propriedades de um objeto ( Form e Controles ), clique no objeto e aperte F4.
:: Para navegar entre as proprieades de um objeto, segure as teclas CTRL + SHIFT + [Letra]
:: Caixa de Ferramentas ( ToolBox ) - CTRL + T para adicionar novo componente.
- Clique duplo no controle para adionar ao formulário ou clique no controle e arraste o mouse no formulário.
Janela de Projeto (Project Explorer - CTRL + R)
Janela de Propriedades (Properties Window - F4)
Exercícios Propostos ( Pág: 15 )
Criar um projeto Standat projetando vários controles sobre o formulário.
Exercícios Propostos 2
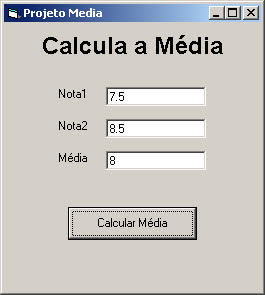
Criar um programa que solicite 2 Notas e calcule e exiba ao usuário a média.
Obs: Utilize a função Val() para converter as notas em número.
Private Sub cmdMedia_Click()
'Utilizar a Função Val() para converte as notas para número
txtMedia.Text = (Val(txtNota1.Text) + Val(txtNota2)) / 2
End Sub
Exercícios Propostos ( Pág: 33 )
Desenvolvar um Projeto programa que o usuário forneça a cidade e uma data, e o programa mostre em um label a data completa.
Ex: Ribeirão Preto, 23 de Outubro de 2009.
Obs: Utilize & ( e comercial ) para concatenar o texto, o comando condicional Select Case para converte o mês para extenso e as funções Day(), Month() e Year().
Private Sub cmdResultado_Click()
Select Case Month(txtData)
Case 1: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Janeiro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 2: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Fevereiro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 3: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Março de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 4: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Abril de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 5: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Maio de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 6: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Junho de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 7: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Julho de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 8: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Agosto de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 9: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Setembro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 10: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Outubro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 11: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Novembro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 12: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Dezembro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
End Select
End Sub
Introdução a Programação do Visual Basic (Cap: 2)
Dica
:: Utilize sempre Option Explicit para trabalhar com variáveis.
:: Declaramos variáveis com Dim.
Disciplina: Linguagem de Programação ( Visual Basic )
Carga Horária: 76 Hrs
Docente Responsável: Francismar Nascimento
Apresentação do Ambiente de Trabalho do Visual Basic (Cap: 1)
Projeto
Apresentação do Ambiente de Trabalho do Visual Basic
Para salvar o Projeto (File / Save Project )
Para abrir um Projeto Existente ( File / OPen Projec
t - CTRL + O)
Para fechar o Projeto atual (ALT + F4)
Formulário
Para Salvar Formulário ( File / Save - CTRL + S)Dicas Gerais
:: Para abrir as janelas de propriedades de um objeto ( Form e Controles ), clique no objeto e aperte F4.
:: Para navegar entre as proprieades de um objeto, segure as teclas CTRL + SHIFT + [Letra]
Janelas
- Clique duplo no controle para adionar ao formulário ou clique no controle e arraste o mouse no formulário.
Janela de Projeto (Project Explorer - CTRL + R)
Janela de Propriedades (Properties Window - F4)
Exercícios Propostos ( Pág: 15 )
Criar um projeto Standat projetando vários controles sobre o formulário.
Criar um programa que solicite 2 Notas e calcule e exiba ao usuário a média.
Obs: Utilize a função Val() para converter as notas em número.
Private Sub cmdMedia_Click()
'Utilizar a Função Val() para converte as notas para número
txtMedia.Text = (Val(txtNota1.Text) + Val(txtNota2)) / 2
End Sub
Exercícios Propostos ( Pág: 33 )
Desenvolvar um Projeto programa que o usuário forneça a cidade e uma data, e o programa mostre em um label a data completa.
Ex: Ribeirão Preto, 23 de Outubro de 2009.
Obs: Utilize & ( e comercial ) para concatenar o texto, o comando condicional Select Case para converte o mês para extenso e as funções Day(), Month() e Year().
Private Sub cmdResultado_Click()
Select Case Month(txtData)
Case 1: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Janeiro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 2: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Fevereiro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 3: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Março de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 4: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Abril de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 5: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Maio de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 6: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Junho de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 7: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Julho de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 8: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Agosto de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 9: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Setembro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 10: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Outubro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 11: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Novembro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
Case 12: lblResultado.Caption = txtCidade.Text & "," & Day(txtData.Text) & " de Dezembro de " & Year(txtData.Text)
End Select
End Sub
Introdução a Programação do Visual Basic (Cap: 2)
Variávies
Dica
:: Utilize sempre Option Explicit para trabalhar com variáveis.
:: Declaramos variáveis com Dim.
Tipos de Dados
| Tipo | Tamanho | Faixa de valores | Prefixo | Exemplo |
| Byte | 1 bytes | 0 to 255 | byt | bytContador |
| Integer | 2 bytes | -32,768 to 32,767 | int | intQuantidade |
| Long | 4 bytes | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,648 | lng | lngToneladas |
| Single | 4 bytes | Negative values: -3.402823E+38 to -1.401298E-45 Positive values: 1.401298E-45 to 3.402823E+38 | sng | sngValorPi |
| Date | 8 Bytes | January 1, 100 to December 31, 9999 | dtm | dtmData |
| Boolean | 2 bytes | True ou False | bln | blnAtivado |
| Variant | 16 bytes | Any value as large as Double (numeric) | vnt | vntValor |
| String | 10 bytes + 1 byte por caracter | 0 to 2 billion characters (variable length) | str | strNome |
Conversão de Tipos
Tipos de Variáveis
Francismar Nascimento da Silva
0
comentários
Tipo da variável Faixa de valor a armazenar
Integer -32.768 a 32.767
Long -2.147.483.648 a 2.147.483.647
Single -3.402823E38 a 3.402823E38
Date/Time 01/01/0100 a 31/12/9999
String 0 a 2 bilhões de caracteres
Boolean True ou False
Byte 0 a 255
Variant Qualquer valor numérico até um double
Variant Qualquer valor numérico até um double
Operadores Lógicos
Francismar Nascimento da Silva
0
comentários
Abaixo as tabelas verdade para os operadores lógicos AND, OR e NOT.
Operador AND
A | B | A AND B |
V | V | V |
V | F | F |
F | V | F |
F | F | F |
Operador OR
A | B | A OR B |
V | V | V |
V | F | F |
F | V | F |
F | F | F |
Operador NOT
A | NOT A |
V | F |
F | V |
Notação Húngara
Francismar Nascimento da Silva
0
comentários
| Control type | prefix | Example |
| 3D Panel | pnl | pnlGroup |
| ADO Data | ado | adoBiblio |
| Animated button | ani | aniMailBox |
| Check box | chk | chkReadOnly |
| Combo box, drop-down list box | cbo | cboEnglish |
| Command button | cmd | cmdExit |
| Common dialog | dlg | dlgFileOpen |
| Communications | com | comFax |
| Control (used within procedures when the specific type is unknown) | ctr | ctrCurrent |
| Data | dat | datBiblio |
| Data-bound combo box | dbcbo | dbcboLanguage |
| Data-bound grid | dbgrd | dbgrdQueryResult |
| Data-bound list box | dblst | dblstJobType |
| Data combo | dbc | dbcAuthor |
| Data grid | dgd | dgdTitles |
| Data list | dbl | dblPublisher |
| Data repeater | drp | drpLocation |
| Date picker | dtp | dtpPublished |
| Directory list box | dir | dirSource |
| Drive list box | drv | drvTarget |
| File list box | fil | filSource |
| Flat scroll bar | fsb | fsbMove |
| Form | frm | frmEntry |
| Frame | fra | fraLanguage |
| Gauge | gau | gauStatus |
| Graph | gra | graRevenue |
| Grid | grd | grdPrices |
| Hierarchical flexgrid | flex | flexOrders |
| Horizontal scroll bar | hsb | hsbVolume |
| Image | img | imgIcon |
| Image combo | imgcbo | imgcboProduct |
| ImageList | ils | ilsAllIcons |
| Label | lbl | lblHelpMessage |
| Lightweight check box | lwchk | lwchkArchive |
| Lightweight combo box | lwcbo | lwcboGerman |
| Lightweight command button | lwcmd | lwcmdRemove |
| Lightweight frame | lwfra | lwfraSaveOptions |
| Lightweight horizontal scroll bar | lwhsb | lwhsbVolume |
| Lightweight list box | lwlst | lwlstCostCenters |
| Lightweight option button | lwopt | lwoptIncomeLevel |
| Lightweight text box | lwtxt | lwoptStreet |
| Lightweight vertical scroll bar | lwvsb | lwvsbYear |
| Line | lin | linVertical |
| List box | lst | lstPolicyCodes |
| ListView | lvw | lvwHeadings |
| MAPI message | mpm | mpmSentMessage |
| MAPI session | mps | mpsSession |
| MCI | mci | mciVideo |
| Menu | mnu | mnuFileOpen |
| Month view | mvw | mvwPeriod |
| MS Chart | ch | chSalesbyRegion |
| MS Flex grid | msg | msgClients |
| MS Tab | mst | mstFirst |
| OLE container | ole | oleWorksheet |
| Option button | opt | optGender |
| Picture box | pic | picVGA |
| Picture clip | clp | clpToolbar |
| ProgressBar | prg | prgLoadFile |
| Remote Data | rd | rdTitles |
| RichTextBox | rtf | rtfReport |
| Shape | shp | shpCircle |
| Slider | sld | sldScale |
| Spin | spn | spnPages |
| StatusBar | sta | staDateTime |
| SysInfo | sys | sysMonitor |
| TabStrip | tab | tabOptions |
| Text box | txt | txtLastName |
| Timer | tmr | tmrAlarm |
| Toolbar | tlb | tlbActions |
| TreeView | tre | treOrganization |
| UpDown | upd | updDirection |
| Vertical scroll bar | vsb | vsbRate |
Suggested Prefixes for Data Access Objects (DAO)
Use the following prefixes to indicate Data Access Objects.
| Database object | Prefix | Example |
| Container | con | conReports |
| Database | db | dbAccounts |
| DBEngine | dbe | dbeJet |
| Document | doc | docSalesReport |
| Field | fld | fldAddress |
| Group | grp | grpFinance |
| Index | ix | idxAge |
| Parameter | prm | prmJobCode |
| QueryDef | qry | qrySalesByRegion |
| Recordset | rec | recForecast |
| Relation | rel | relEmployeeDept |
| TableDef | tbd | tbdCustomers |
| User | usr | usrNew |
| Workspace | wsp | wspMine |
Some examples:
Dim dbBiblio As Database
Dim recPubsInNY As Recordset, strSQLStmt As String
Const DB_READONLY = 4 ' Set constant.
'Open database.
Set dbBiblio = OpenDatabase("BIBLIO.MDB")
' Set text for the SQL statement.
strSQLStmt = "SELECT * FROM Publishers WHERE & _
State = 'NY'"
' Create the new Recordset object.
Set recPubsInNY = db.OpenRecordset(strSQLStmt, _
dbReadOnly)
Suggested Prefixes for Menus
Applications frequently use many menu controls, making it useful to have a unique set of naming conventions for these controls. Menu control prefixes should be extended beyond the initial "mnu" label by adding an additional prefix for each level of nesting, with the final menu caption at the end of the name string. The following table lists some examples.
| Menu caption sequence | Menu handler name |
| File Open | mnuFileOpen |
| File Send Email | mnuFileSendEmail |
| File Send Fax | mnuFileSendFax |
| Format Character | mnuFormatCharacter |
| Help Contents | mnuHelpContents |
When this naming convention is used, all members of a particular menu group are listed next to each other in Visual Basic’s Properties window. In addition, the menu control names clearly document the menu items to which they are attached.
Variable Scope Prefixes
As project size grows, so does the value of recognizing variable scope quickly. A one-letter scope prefix preceding the type prefix provides this, without greatly increasing the size of variable names.
| Scope | Prefix | Example |
| Global | g | gstrUserName |
| Module-level | m | mblnCalcInProgress |
| Local to procedure | None | dblVelocity |
A variable has global scope if it is declared Public in a standard module or a form module. A variable has module-level scope if declared Private in a standard module or form module, respectively.
Note Consistency is crucial to productive use of this technique; the syntax checker in Visual Basic will not catch module-level variables that begin with "p."
Constants
The body of constant names should be mixed case with capitals initiating each word. Although standard Visual Basic constants do not include data type and scope information, prefixes like i, s, g, and m can be very useful in understanding the value and scope of a constant. For constant names, follow the same rules as variables. For example:
mintUserListMax 'Max entry limit for User list
'(integer value,local to module)
gstrNewLine 'New Line character
'(string, global to application)
Variables
Declaring all variables saves programming time by reducing the number of bugs caused by typos (for example, aUserNameTmp vs. sUserNameTmp vs. sUserNameTemp). On the Editor tab of the Options dialog, check the Require Variable Declaration option. The Option Explicit statement requires that you declare all the variables in your Visual Basic program.
Variables should be prefixed to indicate their data type. Optionally, especially for large programs, the prefix can be extended to indicate the scope of the variable.
Variable Data Types
Use the following prefixes to indicate a variable's data type.
| Data type | Prefix | Example |
| Boolean | bln | blnFound |
| Byte | byt | bytRasterData |
| Collection object | col | colWidgets |
| Currency | cur | curRevenue |
| Date (Time) | dtm | dtmStart |
| Double | dbl | dblTolerance |
| Error | err | errOrderNum |
| Integer | int | intQuantity |
| Long | lng | lngDistance |
| Object | obj | objCurrent |
| Single | sng | sngAverage |
| String | str | strFName |
| User-defined type | udt | udtEmployee |
| Variant | vnt | vntCheckSum |
v Variable passed by value (local to a routine)
r Variable passed by reference (local to a routine)
Atalhos de Teclado IDE
Atalhos de Teclado IDE
Aqui está uma lista de combinações de teclas de atalho que podem ser utilizadas enquanto desenvolvemos aplicações em VB.
IDE Navigation
F2 Object Browser
F4 Property Window
Shift+F4 Property Pages
F6 Change Window (Split Window Mode)
F7 Code Window
Shift+F7 Object (Design) Window
Ctrl+D Add File
Ctrl+E Menu Editor
Ctrl+G Immediate Window
Ctrl+L Call Stack (When in RUN mode)
Ctrl+R Solutions Explorer
Ctrl+T Component Window
Ctrl+PgUp Go to Previous Sub/Function/Property (Declaration Line)
Ctrl+PgDn Go to Next Sub/Function/Property (Declaration Line)
Ctrl+Up Go to Previous Sub/Function/Property (First Line after Declaration)
Ctrl+Dn Go to Next Sub/Function/Property (First Line after Declaration)
Code Navigation
Shift+F2 Definition
Ctrl+Shift+F2 Last Cursor Position
F3 Find Next (Last searched item)
Shift+F3 Find Previous (Last searched item)
Ctrl+F3 Find Next (Current Selection)
Ctrl+Shift+F3 Find Previous (Current Selection)
Shift+F10 Context Menu (occasional erratic behaviour, use ContextMenuKey instead)
Form Designer
Shift+Arrow Resize Control
Ctrl+Arrow Move Control (Direction)
Code Edit Shortcuts
Ctrl+Space Complete Word
Ctrl+J List Properties/Methods
Ctrl+Shift+J List Constants
Ctrl+I Quick Info
Ctrl+Shift+I Parameter Info
Run
F5 Start/Continue
Ctrl+F5 Start with Full Compile
Ctrl+Break Break
Shift+F5 Restart
Debug
F8 Step Into
Shift+F8 Step Over
Ctrl+Shift+F8 Step Out
Ctrl+F8 Run To Cursor
Ctrl+W Edit Watch
Shift+F9 Quick Watch
F9 Add/Remove Breakpoint
Ctrl+Shift+F9 Clear All Breakpoints
Ctrl+F9 Set Next Statement
Ctrl+RightArrow Show End Variable Value (tooltip displying variable value is truncated,
use left arrow to view start again)
Categories
- Atualizações (1)
- Aula1 (2)
- IDE (1)
- Notação Húngara (1)
- Operadores (1)
- Projetos (1)
- Tipos de Variáveis (2)
Designed by My Mobiles - Converted to Blogger by Dante Araujo - Supported by Deluxe Templates